Isolated fracture of upper or lower limb can be given first aid at a peripheral referral centres or home in the form of:-

Once the help arrives every injured patient should be shifted to the emergency department of tertiary care centre where he will be thoroughly examined by an emergency doctor. A primary and secondary surveys will be carried out to assess the nature and severity of injuries. For isolated bone fractures an X-rays examination of the injured part will be advised to see the location, type and nature of fractures. Occasionally an MRI or CT scan is also advised to identify the occult injury to bone or soft tissue and to further plan the surgery if needed.
Fractures can be treated without surgery with rest, plaster casts, tractions, various splints or braces, or with surgery depending upon the location, type and severity of bone fracture. Conservative treatment is successful in undisplaced or minimally displaced fractures. Some displaced fractures can be treated without surgery if they can be reduced with manipulative techniques and held in plaster casts under sedation.
Orthoexcellence provides latest minimally invasive nailing techniques for long bone fractures e.g., thigh Bone (Femur) and shin bone (Tibia) and arm Bone (Humerus). A nail is a stainless steel or Titanium rod specifically designed for specific bone which is inserted into the central hollow part of the bone and held in place using screws into the bone and rod so that it doesn't allow motion at broken bone ends allowing early mobilization out of the bed.
The surgery is done under regional anaesthesia(Where your lower half of body is numb) or General Anaesthesia(where you are made to fall asleep till the surgery is complete) once you are declared fit for surgery as decided by the anaesthesiologist depending on your current health condition. You will be made to lie supine and the limb secured on special fracture table. A small incision will be given over the side of your hip for thigh bone or front of your knee to expose upper end of thigh bone and upper end of shin bone respectively. A Guide wire is then placed inside central hollow part of the bone. Central hollow part is gradually dilated using motorized reamers upto the desired diameter. Now the appropriate length and thick nail is selected and loaded over a jig and inserted into the hollow can of bone while keeping the broken end of bone as close to each other as possible. The position of nail and reduction of adequacy of fracture reduction is checked under X-rays machine and the nail is secured to the bone with bolts on each sides of the fracture. Now the Jig is removed and bleeding is stopped and wound is sutured and a sterile Antiseptic dressing is applied. You are shifted to recovery room.
In the post-operative period you will be given antibiotics and pain medicines for some days. All patients are allowed toe touch non weight bearing walking with the help of walker as and when they feel comfortable usually after 24 hours of surgery or so. Siting and knee bending exercises are started as early as tolerated by the patient. Most patients are discharged 3-5 days after surgery. Bathing is only allowed after suture removal usually 12thpost-operative day. Rehabilitation in the form of physical therapy will begins immediately after surgery and an aggressive Orthoexcellence rehab protocol is followed and advised to every patient which is followed till the patient regains muscle strength and full motion while at home. Full weigh bearing walking is started when there is clear evidence of bone healing as seen in the serial post-operative X-rays.
Plating is a method of fracture fixation where the fracture bone ends are held in place using a stainless steel or titanium plate fixed to bone using screws on either side of the fracture. Plate can be placed after fully exposing the fractured bone ends or using the minimally invasive techniques where indirect reduction is done and plate is slid across the fracture site using small incisions. Screws alone are used to get hold of small bone fragments, bony avulsions, and small bone fractures. Plates and screws commonly recommended for the fracture of following bones
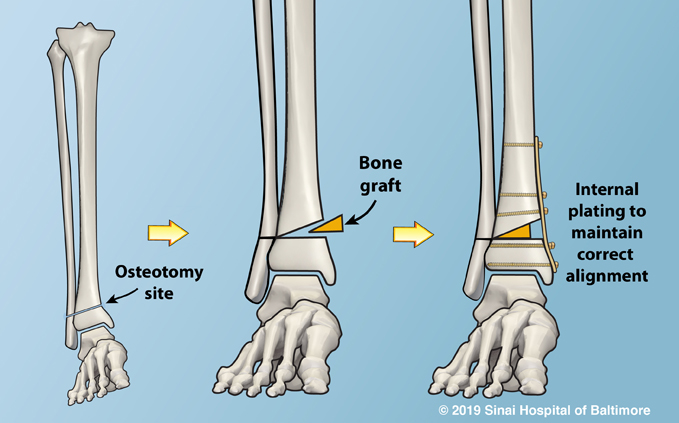
Depends on the location, fracture type and nature of surgery performed. Antibiotics and pain medication is given for few days. A plaster cast, sling or a brace may be worm for some time after suture. Usually joint motion is started as early as possible when the effect of anaesthesia is over to prevent stiffness in the joints. Patients are discharged 3-5 days after surgery. Full function is allowed gradually over few months once bone is fully united as evidenced by the serial X-ray images. Fracture around the joints require aggressive physiotherapy rehabilitation to regain motion and strength in the limb.
Kirschner or K wire is a thin stainless steel or titanium wire which can be used to hold a reduced fractures. You will be made to sleep completely before putting wires. These are usually inserted across the fracture ends using minimally invasive techniques directly piercing your skin. The displaced fracture is first reduced and an attempt is made to align the fracture fragments as completely as possible, then the reduced fracture fragments are held with wires in place till the natural fracture healing starts. They can be buried under your skin or left outside the skin. You limb may be placed in a plaster cast for few weeks after K wire fixation. Patients is usually discharged from hospital the same day or 48 hours after the surgery. Most K-wires are removed 6-8 weeks after your surgery. You may need admission for wire removal but most wires can be pulled in the Outpatient settings with or without numbing your limb. Commonly treated fractures with K wires are,hand and finger bone fracture, Shoulder ( Humerus ) fractures in elderly, Wrist fractures, some elbow fractures.
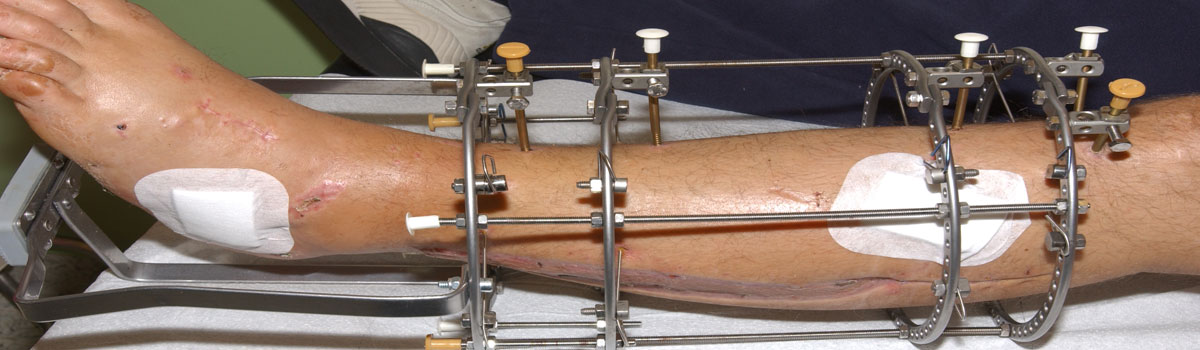
External fixators are made of stainless steel hollow rods of various sizes, long and short screw pins and clamps which are used to fix rods with the pins. These devices help to stabilize the fractured bones while remaining external to the body. These are mostly used for fracture where there is loss of tissue to adequately cover the fracture ends, in infected fractures etc.
Screw pins are inserted on either side of the fracture ends giving small stab cuts on the health skin away from wound. These screws are fixed to the hollow tubes of desired length using fixation clams outside you skin. The wounds are cleaned, washed, dirty tissues are removed and bones and other vital structure are covered as much as possible. External fixators allow easy access to the wound and are kept as long as the wound heals. Sometimes these are also applied in fractures near the joint with there is huge swelling due to high energy injury. In such cases fixators help to give rest to the injured part while reducing pain, swelling and are kept till the swelling is reduced to extend that the final surgery can be performed. Although they can be kept as long as the bone is fully united but most of the times once the soft of the limb is healthy and healed fixators are removed and the fracture are operated and definitive nailing or plating is done in second surgery.
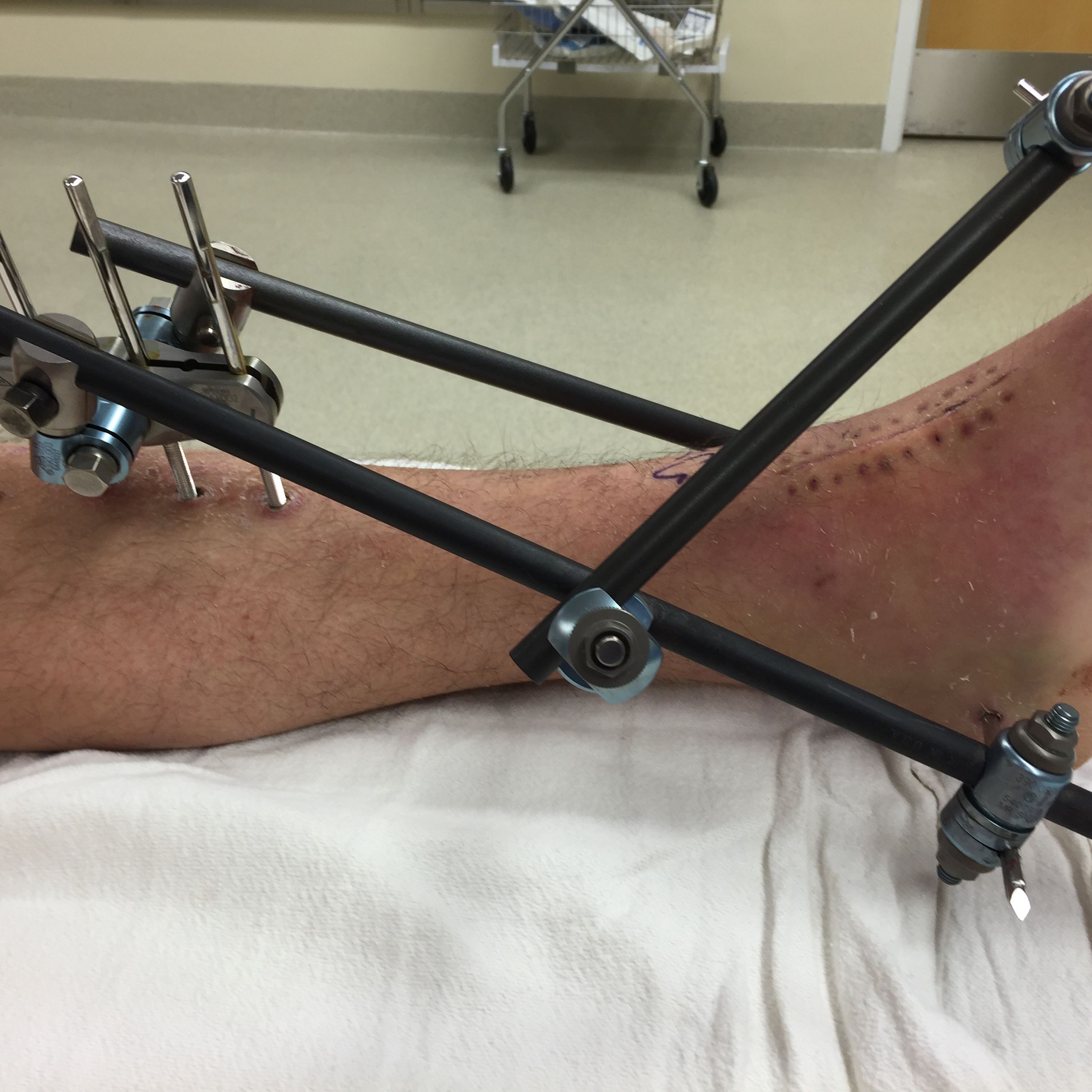
It is a type of external fixator and consists of large stainless steel half rings of various sizes, screw pins, arches, nuts and bolts, post and plates, trans fixation wires, rods, telescoping tubes etc. Most of the parts are outside of the bone of the patient except for the screw pins, and transfixing wires which connect the bone with the rings. The frame so constructed provides stability to the fracture in proper position and is strong enough to allow early weight bearing. It can also be used to lengthen short bones. An initial surgery is conducted and the short bone is artificially fractured at desired position and ring fixator is applied. The limb can gradually be lengthened by tightening and loosening the nuts so that the distance between two rings is gradually increased. This gradual distraction promotes bone formation and lengthening. Once the desired limb length is achieved distraction is stopped and the new bone is allowed to solidify after which the frame is removed. Deformities of limbs can also be corrected by variations of distraction and compression of rings one both sides of the bone.